Vaginal boils can be a painful and uncomfortable condition for women. Boils are caused by infected hair follicles and are typically located in the pubic area. They can be difficult to treat and can cause serious health problems if left untreated. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for vaginal boils.
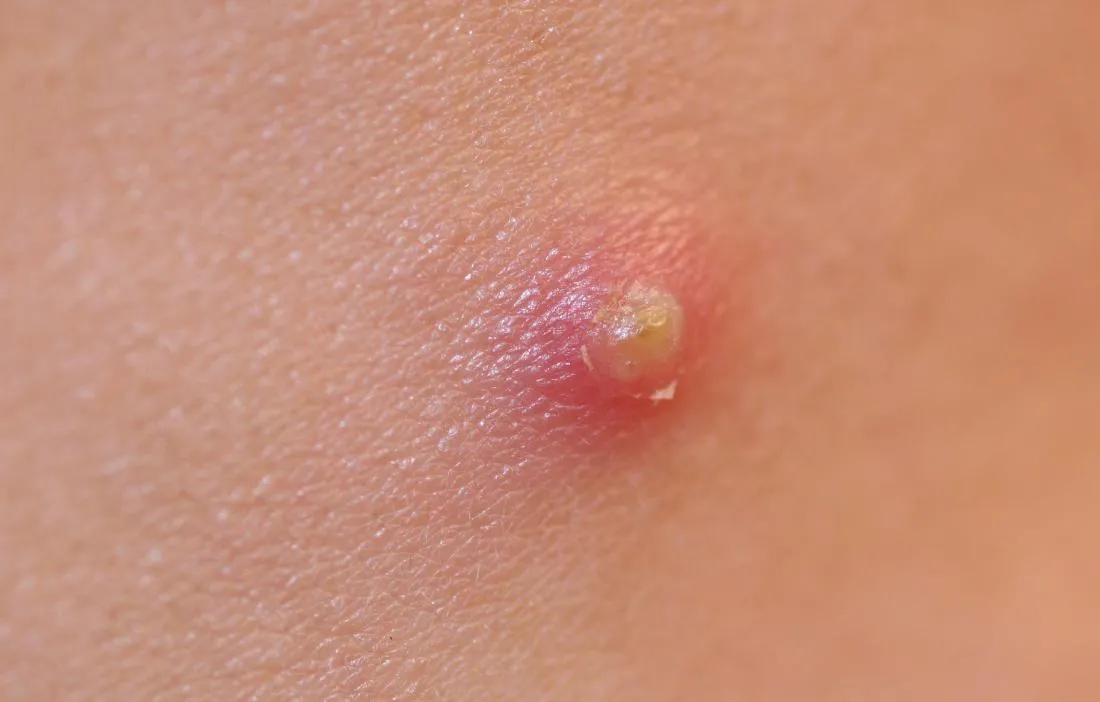
What is Vaginal Boil?
A vaginal boil is a painful, pus-filled bump that develops on the skin in the pubic area. They are caused by bacteria that infect hair follicles (folliculitis) and cause them to become inflamed. Boils can be small or large, and they can appear individually or in clusters.
Causes of Vaginal Boil
There are several factors that can increase a woman’s risk of developing a vaginal boils. Some of the popular causes include:
Poor hygiene
Poor hygiene practices, such as not washing the pubic area regularly or wearing tight clothing, can create a warm, moist environment that is ideal for bacteria to grow.
Hormonal changes
Hormonal changes, such as those experienced during menstruation or pregnancy, can cause the skin in the pubic area to become more sensitive and vulnerable to infection.
Weak immune system
A weak immune system can make it more difficult for the body to fight off infections, increasing the risk of developing a vaginal boil.
Other skin conditions
Certain skin conditions, such as Eczema or Psoriasis, can make the skin more susceptible to infection and increase the risk of developing boils.
Symptoms of Vaginal Boil
The most common symptom of a vaginal boil is a painful, red bump on the skin. Other symptoms can include:
- Swelling in the affected area
- Pain or tenderness when touched
- Drainage of pus or other fluids from the boil
- Redness and warmth in the affected area
- Fever
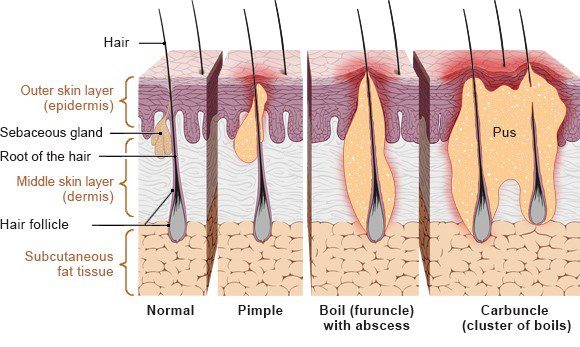
Diagnosis of Vaginal Boils
Diagnosis of a vaginal boil is typically done by a doctor or nurse practitioner. They will examine the affected area and ask about symptoms and medical history. In some cases, a sample of the pus from the boil may be taken for testing (Pus culture and sensitivity test) to determine the type of bacteria causing the infection.
Treatment of Vaginal Boil
Treatment for vaginal boils typically involves a combination of antibiotics and home care. Some of the accepted treatment options include:
Home care
Applying a warm compress to the affected area and keeping the area clean and dry can help to reduce pain and promote healing.
Wear loose-fitting bottoms while you heal to reduce friction.
Do not pick or pierce a boil. Opening a boil can release bacteria and spread the infection. It can also aggravate pain and sensitivity.
Wash your hands with antibacterial soap and warm water before touching the boil or the area around it. This will prevent new bacteria from entering in the boil. Also, wash your hands after touching a boil to prevent the infection from spreading to other parts of your body.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics can help to reduce the severity of symptoms and speed up the healing process.
Drainage
If the boil is large or painful, it may need to be drained. This is typically done by a doctor or nurse practitioner.
Preventing Vaginal Boil
There are several steps women can take to reduce their risk of developing vaginal boils. Some of the practical measures include:
- Good hygiene: Keeping the pubic area clean and dry can help to reduce the risk of infection.
- Wearing loose clothing: Wearing loose clothing can help to reduce friction and irritation in the pubic area, reducing the risk of developing boils.
- Maintaining a healthy immune system: Eating a healthy diet, getting plenty of rest, and avoiding stress can help to maintain a strong immune system and reduce the risk of infection.
- Washing your hands regularly also helps reduce your bacterial exposure.
- Not sharing personal items: You can reduce the risk of infection by not sharing personal items such as towels and underwear.
Read more: 9 cluster headache home remedy
When To See Doctor
Women should see a doctor if the boil does not respond to home remedies or over-the-counter medications or if it seems to be getting worse instead of improving. Women should also seek treatment if they notice signs of infection, such as bloody pus, boils, or surrounding skin that is hot to the touch. Anyone with signs of systemic infection, such as fever, should also see a doctor.
Our Take on Vaginal Boil
In conclusion, a vaginal boil is a painful and uncomfortable condition that can be caused by a variety of factors. With proper treatment and preventative measures, however, women can reduce their risk of developing this condition.
Most boils in the vaginal area shrink and disappear within a few weeks and respond to home treatment. However, some boils do not respond to self-treatment. If you notice that your vaginal boil hasn’t improved, is getting worse, or shows signs of infection, it’s important to see your doctor. Larger, more severe vaginal boils or infected ones should be incised and drained and possibly treated with antibiotics.




