Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is an important organ that processes nutrients, fights infections, and filters blood. If the liver is inflamed or damaged, it can affect its function. Heavy alcohol consumption, poisons, certain medications, and certain diseases can cause hepatitis.
Hepatitis ABC Difference: Hepatitis is usually caused by a Virus called Viral Hepatitis. The 3 common types of Viral Hepatitis are:
- Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C
What Is Hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver. The condition may resolve on its own or progress to fibrosis (scarring), liver cancer, or liver cirrhosis. Hepatitis viruses are the prevalent cause of hepatitis in the world.
When the hepatitis virus enters the human body, it travels to the liver. It can then enter the liver cells and begin to multiply, producing more of itself. Then the virus starts to damage your liver cells. This activates the body’s defense system and starts Immune cells (WBCs) to begin migrating to the liver to fight the infection. This action of the body’s defense mechanism also promotes inflammation.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Viral Hepatitis
Most of people with hepatitis have no symptoms and do not know they are infected. If symptoms develop with an acute infection, they may appear anytime between 2 weeks and 6 months after exposure. Symptoms of chronic viral hepatitis can take one or more decades to appear. Symptoms include:
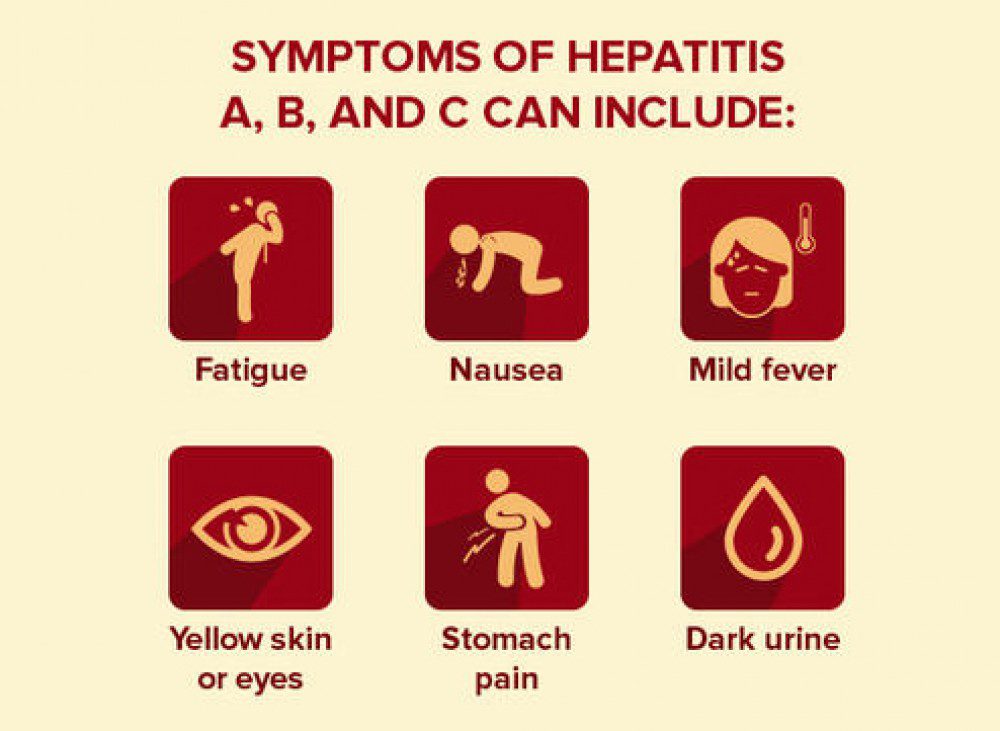
- Jaundice
- Fatigue
- Nausea/ vomiting
- Fever
- Abdominal pain (mostly upper right sided)
- Loss of appetite
- Light-colored stools
- Joint pain
- Dark colored urine
What is Hepatitis A
- It is caused by the Hepatitis A Virus (HAV).
- Most patients with the acute disease recover without permanent liver damage; Death is rare but more common in the elderly and/or people with underlying liver disease.
- It is available in the feces of infected people and is most commonly spread by consuming contaminated water or food. It transfers by the fecal-oral route.
- Having close contact with Hepatitis A Virus carrier(patients) like taking care of them, or having sex with them also spreads HAV.
- Touching contaminated objects, such as toilets and not washing hands after that also spreads HAV.
- Incubation period: (The period between exposure to an infection and the appearance of the first symptoms) 15-50 days. (Average 28 days) (1)
Risk Factors of Viral Hepatitis A
There are several risk factors for Hepatitis A, including:
- Close personal contact with an infected person
- Consuming contaminated food or water
- Travel to the areas with higher rates of hepatitis A
- Living in overcrowded or unsanitary conditions
- Being a man who has sex with the man
- Using illicit drugs (injected or non-injected)
- Having a history of liver disease
- Being a household member or caregiver for a person with hepatitis A
- Being a child in a group childcare setting
- Homelessness or unstable housing
- Being a staff member or resident in a correctional facility.
- It should be noted that not all people with risk factors will contract hepatitis A and others may contract the disease without any known risk factors.
Risk for severe disease
These are the people with severe risk of disease:
- People suffering from Chronic liver disease like Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C
- People suffering from HIV
- Older peoples
Hepatitis A Treatment
Hepatitis A has no such specific treatment. It is treated symptomatically like for Fever, Pain acetaminophen (paracetamol); for Nausea/Vomiting Ondansetron; Fluids, Healthy diet, Proper rest.
How To Prevent Hepatitis A
- By giving Hepatitis A vaccine to all children aged 12-23 months, children and adolescents 2–18 years of age who have not previously received vaccine, and all high risk category peoples.
- Proper hand washing.
- Maintaining hygiene of food and water.
What is Hepatitis B
- It is caused by the Hepatitis B Virus (HBV).
- 15%–25% of people with chronic infection can develop the chronic liver disease; including liver cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer.
- It is transmitted by contact with blood, semen, and other infectious body fluids. E.g. By sexual contact with an HBV-infected person.
- The Hepatitis B virus can be passed from an infected mother to a child at birth, or from family members to a child in early childhood.
- Transmission can also occur through blood transfusions contaminated with Hepatitis B.
- Hepatitis B also has a risk to healthcare workers who suffer accidental needle-stick injuries while caring for patients with the hepatitis B virus.
- Sharing personal things that may have come into contact with blood or other body fluids, such as razors, syringes, needles, drug preparation equipment’s and toothbrushes.
- Incubation period: 60-150 days. (Average 90 days) (2)
Risk Factors of Viral Hepatitis B
- Whose spouse/ sex partner is Hepatitis B positive
- Being a man who has sex with the man
- Occupational exposure- Healthcare workers (needle-stick injury)
- Infant which is born to HBsAg +ve mother
- People taking injectable drugs
- People with HIV +ve
- Pregnant women
- People on dialysis or end stage kidney disease
Risk for severe disease
These are the people with severe risk of disease:
- Pregnant women
- Older people
- People suffering from HIV
- People with chronic kidney diseases
- People with chronic liver diseases
Hepatitis B Treatment
- Acute Hepatitis B- There are no medications for acute infection, like hepatitis A only supportive treatment is given.
- Chronic Hepatitis B- Monitor regularly for signs of liver disease progression from the Physician; also, some antiviral drugs are available.
How To Prevent Hepatitis B
- By giving Hepatitis B Vaccine to all infants, all non-vaccinated children & adolescents <19 years, & all high-risk category people.
What is Hepatitis C
- It is caused by the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV).
- It is transmitted mainly by contact with infected blood. This can happen through blood transfusions contaminated with the hepatitis C virus, contaminated injection fluids during medical procedures and the use of injections.
- It can also transmit by sexual contact with HCV infected person (less common).
- The Hepatitis C virus can be passed from an infected mother to a child at birth (less common).
- Needle-stick injury (less common)
- Incubation period: 14-182 days. (Average 14-84 days) (3)
Risk Factors of Viral Hepatitis C
- Whose spouse/ sex partner is Hepatitis C positive
- Occupational exposure- Healthcare workers (needle-stick injury)
- Infant which is born to HCV +ve mother
- People taking injectable drugs
- People with HIV +ve
- Pregnant women
- People on dialysis or end stage kidney disease
Risk for severe disease
These are the people with severe risk of disease:
- According to CDC over 50% of newly infected people can develop Chronic infection with HCV.
- Pregnant women
- Older people
- People suffering from HIV
- People with chronic kidney diseases
- People with chronic liver diseases
Hepatitis C Treatment
- More than 90% of people infected with HCV recover within 8 to 12 weeks of oral anti-viral treatment, regardless of HCV genotype.
- At present the same antiviral medications are recommended for both acute and chronic Hepatitis C.
How To Prevent Hepatitis C
- There is no Hepatitis C Vaccine for HCV
- Proper hand washing
- Use of contraception.
Takeaway from Hepatitis ABC difference
FAQs
-
Can Hepatitis B Treated Completely?
Once hepatitis occurs, it cannot be cured. Treatment aims to prevent further damage to the liver, reverse existing damage as much as possible, and relieve symptoms. Most cases of acute hepatitis resolve with time.
-
Can I Still Get Hepatitis B Even if I was Vaccinated?
Hepatitis B can be prevented with a vaccine. This means that once the series of vaccines is completed, you will not be infected by hepatitis B under any circumstances, and you will be guaranteed for life! However, it is important to remember that vaccines are only effective if the person has not been previously infected.
Some studies have shown that immunologic memory in healthy people who start hepatitis B vaccine at >6 months of age remains intact for at least 30 years.(4)
-
Is There a Vaccine to Protect Me From Hepatitis Infections?
There are vaccines for Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B, but no vaccine for Hepatitis C.
-
My Husband Has Hepatitis A Can I Get It?
Yes, Hepatitis A virus transmission can occur during any sexual activity with an HAV infected person and is not limited to fecal-oral contact. Sexually active people are considered at high risk of contracting hepatitis A.
-
Can Kissing Give You Hepatitis B?
According to CDC using Latex condoms during sex can protect against HAC.
Read More: 9 cluster headache home remedy


3 thoughts on “Hepatitis ABC Difference: Understand the difference and protect yourself (2023)”