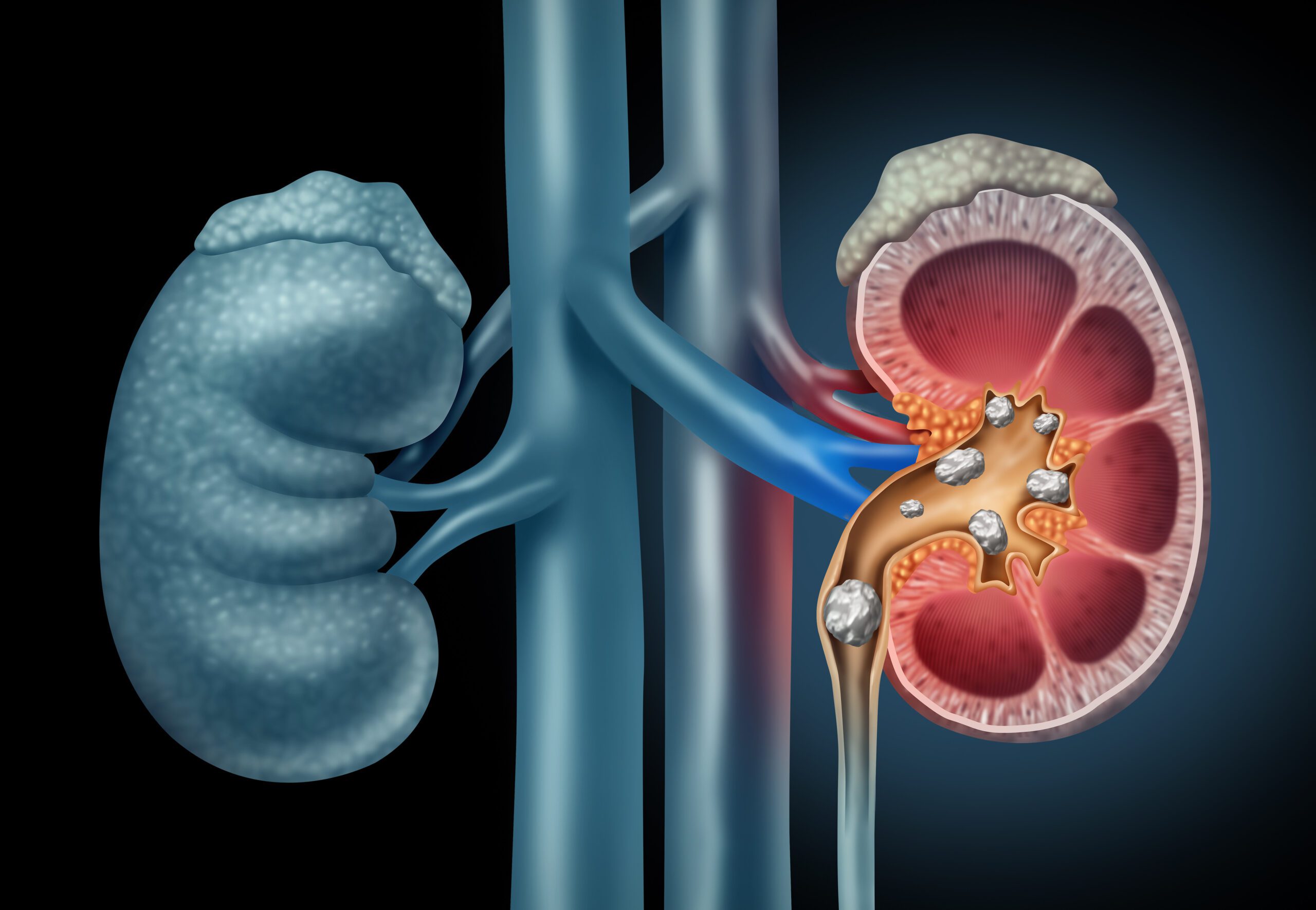
Definition of kidney stone
Kidney stones (also known as Renal Calculi, Nephrolithiasis, or Urolithiasis) are solid deposits of minerals and acid salts that form in the kidneys or urinary tract. The size of kidney stones can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters. 7mm kidney stones are considered large and can cause severe pain and discomfort when they get stuck in the urinary tract. (1)
The incidence of 7mm kidney stones is not uncommon, and many people experience them at some point in their lives. They can affect both men and women, but men tend to develop them more frequently.
In addition, people who have a history of kidney stones are more likely to develop them again, including 7mm kidney stones. Overall, understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for 7mm kidney stones is essential for early diagnosis and proper management of this condition.
Symptoms of 7mm kidney stones
A kidney stone can cause several symptoms that can be severe and interfere with daily life. Some common symptoms include:
- Pain in the back or side:
The most common symptom of a kidney stone is pain, which can be felt in the back or side of the body. The pain can be sharp, sudden, and intense, and may come and go in waves.
- Pain during urination:
People with a 7mm kidney stone may experience pain or discomfort when urinating. The pain may be felt in the lower abdomen, groin, or genitals.
- Blood in the urine:
Another symptom of a kidney stone is blood in the urine, which may be visible to the naked eye or only visible under a microscope. This can be a sign of a urinary tract infection or other complications.
- Nausea and vomiting:
7mm kidney stones can cause nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite. These symptoms are typically a result of the body’s response to the intense pain.
- Frequent urination:
People with a 7mm kidney stone may experience an increased urge to urinate, even if only small amounts of urine are produced.
- Fever and chills:
In some cases, a 7mm kidney stone can cause a fever and chills. This can be a sign of an infection or other complications and requires immediate medical attention.
It is important to seek medical attention if any of these symptoms occur, as they can indicate a serious condition that requires prompt treatment.(2)
You May Like: Saddle Pulmonary Embolism: Symptoms You Should Not Ignore
Causes of kidney stones
Kidney stones can develop for a variety of reasons, and several factors can contribute to the formation of a 7mm kidney stone. Some common causes of 7mm kidney stones include:
- Dehydration:
Not drinking enough fluids can lead to the formation of kidney stones. When the body is dehydrated, the urine becomes concentrated, which increases the risk of mineral deposits forming in the kidneys.
- High levels of calcium, oxalate, or uric acid in the urine:
Certain substances in the urine, such as calcium, oxalate, and uric acid, can build up and form kidney stones. High levels of these substances in the urine can increase the risk of developing a 7mm kidney stone.
- Family history of kidney stones:
A family history of kidney stones can increase the likelihood of developing them. Genetic factors can contribute to the formation of kidney stones, including 7mm kidney stones.
- Certain medications:
Some medications can increase the risk of developing kidney stones, including 7mm kidney stones. These medications include diuretics, antacids containing calcium, and certain antibiotics.
- Obesity:
Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing kidney stones, including 7mm kidney stones. Excess weight can lead to an increase in calcium and uric acid levels in the urine, which can contribute to the formation of kidney stones.(3)
Diagnosis of kidney stones
Diagnosing a 7mm kidney stone typically involves a combination of physical exams and imaging tests. Some common diagnostic tests used to detect a 7mm kidney stone include:
- Physical exam:
A physical examination may be conducted to assess the patient’s overall health and identify any signs of a kidney stone, such as pain in the back or side.
- Urine test:
A urine test can be used to detect the presence of blood or minerals in the urine, which can indicate the presence of a kidney stone.
- Blood test:
A blood test can help identify any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to the formation of a kidney stone.
- Imaging tests:
Imaging tests, such as a CT scan, ultrasound, or X-ray KUB, IVP can help detect the presence and location of a 7mm kidney stone. These tests can also help determine the size and shape of the stone, which can guide treatment decisions.(4)
You May Like: 9 cluster headache home remedy: Should Try At Home
Treatment of kidney stones
Treatment for a 7mm kidney stone depends on several factors, including the location, size, and composition of the stone. Some common treatments for 7mm kidney stones include:
- Drinking lots of fluids:
Drinking plenty of fluids, particularly water, can help flush out the kidney stone and alleviate symptoms. It is recommended to drink at least 2 to 3 liters of water per day.
- Pain relief medications:
Over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen, diclofenac, ketorolac or acetaminophen, can help alleviate pain associated with a 7mm kidney stone.
- Medical therapy to break up or dissolve the stones:
Medical therapy may be used to break up or dissolve the kidney stone. This can include extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL), which uses shock waves to break up the stone, or medications that can help dissolve certain types of kidney stones.
- Surgery to remove the stones:
Surgery may be necessary to remove a 7mm kidney stone if other treatments are not effective. This can include ureteroscopy, which involves using a small scope to remove the stone, or percutaneous nephrolithotomy, which involves making a small incision in the back to remove the stone.
It is important to discuss the best treatment options with a healthcare provider, as the appropriate treatment can depend on several factors, such as the size and composition of the kidney stone, the presence of any complications, and the overall health of the patient.(5)
Prevention of kidney stones
Preventing kidney stone from forming can be achieved by making some lifestyle changes. Some ways to prevent the formation of kidney stones include:
- Drinking plenty of water:
Staying hydrated is crucial in preventing the formation of kidney stones.
- Limiting sodium intake:
Consuming too much sodium can increase the risk of developing kidney stones.
- Moderating protein intake:
Consuming too much animal protein can increase the risk of developing kidney stones.
- Avoiding high oxalate foods:
Foods such as spinach, chocolate, and nuts are high in oxalates, which can increase the risk of developing kidney stones.
- Increasing intake of citric acid:
Consuming foods high in citric acid, such as lemons and oranges, helps in preventing the formation of kidney stones.
- Taking medications as prescribed:
If you have a medical condition that increases your risk of kidney stones, such as hypercalciuria or gout, taking medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider can help prevent the formation of kidney stones.
- Getting regular check-ups:
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help detect any underlying medical conditions that may increase your risk of kidney stone formation.(6)
When to See a Doctor for Kidney Stone
If you experience severe pain or other symptoms of kidney stones, it is important to look up medical attention immediately. In some cases, kidney stones can cause complications such as severe pain, nausea-vomiting, fever with chills, blockage of the urinary tract (difficulty in micturition) or blood in urine.
Your doctor may recommend medical treatments or procedures to help alleviate the symptoms and prevent complications.(7)
Conclusion
In summary, a 7mm kidney stone can cause significant pain and discomfort, as well as other symptoms such as blood in the urine and nausea. It is important to seek medical attention promptly if you experience any symptoms of a kidney stone, as early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications.
You May Like: Vaginal Boil: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
FAQs
Can kidney stones pass on their own?
- Small kidney stones may pass on their own through urine without any treatment. However, larger stones may require medical intervention.(8)
How can I prevent kidney stones from forming?
- You can prevent kidney stones from forming by staying hydrated, limiting sodium intake, moderating protein intake, avoiding high oxalate foods, and increasing intake of citric acid.(9)
What are the symptoms of kidney stones?
- Common symptoms of kidney stones include severe pain in the back, side, or lower abdomen, nausea and vomiting, blood in the urine, frequent urination, painful urination, and difficulty passing urine.
How are kidney stones diagnosed?
- Kidney stones are diagnosed through physical exams and tests such as urine tests, blood tests, and imaging tests.
Can kidney stones cause complications?
- Yes, kidney stones can cause complications such as infection, blockage of the urinary tract, or kidney damage. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you experience severe symptoms.(10)
Can a 7mm kidney stone dissolve?
- It is possible for a 7mm kidney stone to dissolve on its own, but it depends on the composition of the stone and other factors such as hydration and medical treatment. In some cases, medical intervention may be necessary to dissolve or remove the stone.(11)
How long does it take for a 7mm kidney stone to form?
- The time it takes for a 7mm kidney stone to form can vary depending on factors such as diet, hydration, and genetics. However, kidney stones generally take weeks to months to form.(12)
Is a 7mm kidney stone dangerous?
- Yes, a 7mm kidney stone can be dangerous if it causes complications such as infection, blockage of the urinary tract, or kidney damage. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience severe symptoms or complications.(13)